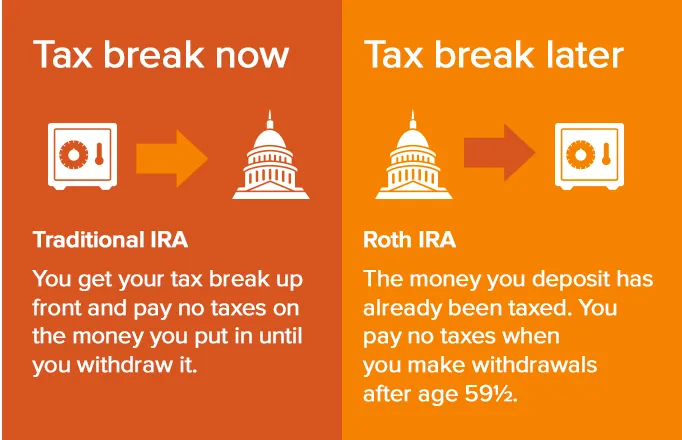
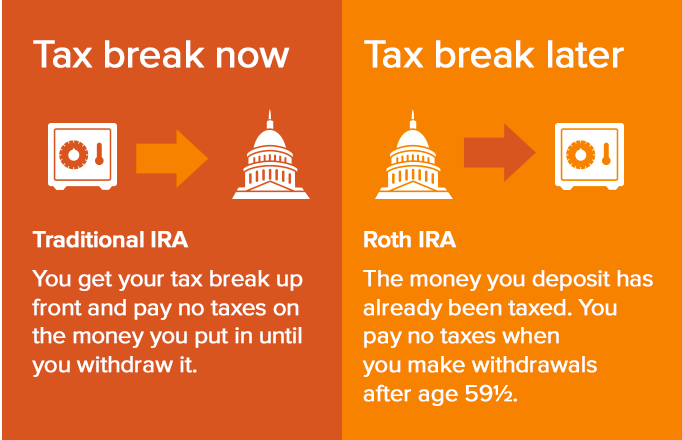
Roth IRA contributions are taxed upfront but grow tax-free. Traditional IRA contributions are tax-deductible but taxed upon withdrawal.
Deciding between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA hinges on your current tax situation and future tax expectations. Roth IRAs offer tax-free growth, making them ideal if you expect higher taxes in retirement. Contributions to Traditional IRAs are tax-deductible, which can lower your taxable income now.
Table of contents
These are beneficial if you anticipate being in a lower tax bracket during retirement. Both options provide tax advantages and potential growth, but their suitability depends on individual financial circumstances. Consider your current income, retirement plans, and tax projections to choose the best IRA for your needs. Make informed decisions to secure your financial future.
Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA is essential for making informed retirement decisions. These two popular retirement accounts have distinct features. Knowing their differences can help you choose the one that fits your financial goals best.
Tax Treatment
The tax treatment of Roth IRAs and Traditional IRAs varies significantly. With a Roth IRA, you contribute money that you’ve already paid taxes on. This means your contributions are made with after-tax dollars. The biggest advantage is that your money grows tax-free. When you withdraw it in retirement, you won’t owe any taxes on the earnings.
In contrast, a Traditional IRA offers a different tax advantage. Contributions to a Traditional IRA are often tax-deductible. This means you can lower your taxable income for the year you make the contributions. Your investments grow tax-deferred. You will pay taxes on the money when you withdraw it in retirement.
| Feature | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Contributions | After-tax dollars | Pre-tax dollars |
| Tax Benefit | Tax-free growth and withdrawals | Tax-deductible contributions |
| Tax on Withdrawals | No tax on qualified withdrawals | Taxed as ordinary income |
This table summarizes the key tax treatment differences. Choosing the right IRA depends on your current tax situation and future expectations.
Withdrawal Rules
Withdrawal rules for Roth IRAs and Traditional IRAs also differ. With a Roth IRA, you can withdraw your contributions anytime, tax-free and penalty-free. This flexibility makes Roth IRAs attractive for those who may need access to their funds before retirement.
For earnings in a Roth IRA, withdrawals are tax-free if you meet two conditions:
- You are at least 59½ years old.
- The account has been open for at least five years.
In contrast, Traditional IRA withdrawals follow stricter rules. Withdrawals before age 59½ typically incur a 10% penalty and are subject to income tax. There are exceptions, such as for first-time home purchases or educational expenses, but these are limited.
Once you reach age 72, required minimum distributions (RMDs) kick in. You must start taking withdrawals, which are taxed as ordinary income. This requirement does not apply to Roth IRAs, offering more flexibility in managing your retirement funds.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Feature | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Early Withdrawals | Contributions: Anytime tax-free | Subject to taxes and penalties |
| Earnings Withdrawals | Tax-free if conditions met | Taxed as ordinary income |
| Required Minimum Distributions | None | Start at age 72 |
Understanding these rules can help you plan your withdrawals to maximize your retirement savings.
Contribution Limits
When choosing between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA, understanding the contribution limits is crucial. Both types of IRAs come with specific rules about how much you can contribute each year. These limits impact your retirement savings strategy significantly. Knowing the details helps you make informed decisions and maximize your retirement benefits.
Annual Limits
The annual contribution limits for both Roth IRA and Traditional IRA are set by the IRS. For the year 2023, the maximum contribution limit is $6,500 for individuals under the age of 50. This limit applies regardless of which type of IRA you choose. Let’s break it down further:
- Roth IRA: The $6,500 limit is subject to income limits. If your income exceeds certain thresholds, your contribution limit may be reduced or eliminated.
- Traditional IRA: The $6,500 limit is not subject to income limits. However, the tax deductibility of your contribution may be affected if you or your spouse have access to a retirement plan at work.
Here’s a quick comparison table:
| IRA Type | Contribution Limit | Income Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Roth IRA | $6,500 | Yes |
| Traditional IRA | $6,500 | No |
These limits apply per individual. If you’re married, both you and your spouse can contribute up to the limit in separate accounts, potentially doubling your retirement savings.
Catch-up Contributions
If you’re 50 or older, the IRS allows you to make catch-up contributions. This helps you save more as you approach retirement. For 2023, the catch-up contribution limit is $1,000.
- Roth IRA: You can contribute an additional $1,000, making the total $7,500 if you are 50 or older.
- Traditional IRA: You also get to contribute an extra $1,000, bringing your total to $7,500.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Age | Roth IRA Limit | Traditional IRA Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Under 50 | $6,500 | $6,500 |
| 50 and Over | $7,500 | $7,500 |
Catch-up contributions are a powerful tool for those who started saving late or want to boost their retirement funds. This extra $1,000 can significantly impact your retirement savings over time.
Eligibility Criteria
Choosing between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA can be confusing. One crucial aspect to consider is the eligibility criteria. Understanding the income limits and filing status requirements can help you make an informed decision about which IRA is best for your financial goals.
Income Limits
The eligibility for Roth IRAs and Traditional IRAs varies based on your income. Here’s a breakdown of the income limits for each:
- Roth IRA: Your ability to contribute to a Roth IRA is affected by your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI). For 2023, the limits are as follows:
| Filing Status | MAGI | Contribution Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Single | Up to $138,000 | Full Contribution |
| Single | $138,001 – $153,000 | Partial Contribution |
| Married Filing Jointly | Up to $218,000 | Full Contribution |
| Married Filing Jointly | $218,001 – $228,000 | Partial Contribution |
- Traditional IRA: There are no income limits for contributing to a Traditional IRA. However, your income can affect your ability to deduct contributions if you or your spouse are covered by a retirement plan at work.
| Filing Status | MAGI | Deduction Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Single | Up to $68,000 | Full Deduction |
| Single | $68,001 – $78,000 | Partial Deduction |
| Married Filing Jointly | Up to $109,000 | Full Deduction |
| Married Filing Jointly | $109,001 – $129,000 | Partial Deduction |
Filing Status
Filing status also plays a significant role in determining your eligibility for both Roth and Traditional IRAs. Here are the details:
- Roth IRA: Your filing status affects the income limits for Roth IRA contributions. The main statuses to consider are:
- Single: Single filers have different income thresholds compared to married filers.
- Married Filing Jointly: Couples who file jointly have combined income limits for Roth IRA contributions.
- Married Filing Separately: This status has stricter limits, often reducing the contribution amounts significantly.
- Traditional IRA: Your filing status can affect the deductibility of your contributions:
- Single: Single filers have specific income ranges for full or partial deductions.
- Married Filing Jointly: Joint filers combine their incomes to determine the deduction limits.
- Married Filing Separately: This status has lower income thresholds for deduction eligibility.
Understanding these eligibility criteria helps you choose the right IRA for your retirement savings. Whether you prefer a Roth IRA or a Traditional IRA, knowing the income limits and filing status requirements ensures you maximize your contributions and tax benefits.
Withdrawal Timing
When deciding between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA, understanding withdrawal timing is crucial. This includes knowing when and how you can take money out of your account. Different rules apply to each type of IRA, and these can affect your tax situation and retirement planning.
Early Withdrawals
Early withdrawals from an IRA refer to taking out money before the age of 59½. Both Roth and Traditional IRAs have specific rules about this. With a Traditional IRA, early withdrawals incur a 10% penalty on top of regular income tax. This can significantly reduce your savings.
In contrast, a Roth IRA allows for more flexibility. You can withdraw contributions (but not earnings) at any time without penalties or taxes. This is because contributions are made with after-tax dollars. However, withdrawing earnings before age 59½ or before the account is five years old can result in penalties and taxes.
- Traditional IRA Early Withdrawals: 10% penalty + income tax
- Roth IRA Early Withdrawals: Contributions anytime tax-free; earnings may incur penalties and taxes
There are exceptions to these penalties for both types of IRAs. These include situations like first-time home purchases, certain medical expenses, and higher education costs. Knowing these exceptions can help you make more informed decisions about early withdrawals.
Retirement Withdrawals
Retirement withdrawals begin at age 59½ or later. The rules differ significantly between Roth and Traditional IRAs. With a Traditional IRA, you must start taking required minimum distributions (RMDs) at age 73. These withdrawals are taxed as regular income.
In contrast, a Roth IRA does not require RMDs during the account holder’s lifetime. This allows your money to continue growing tax-free. Additionally, qualified distributions from a Roth IRA (after age 59½ and the account being at least five years old) are tax-free.
| Type of IRA | RMDs Required? | Tax on Withdrawals |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional IRA | Yes, starting at age 73 | Taxed as regular income |
| Roth IRA | No RMDs during lifetime | Tax-free if qualified |
Planning your retirement withdrawals can have significant tax implications. Using a mix of Roth and Traditional IRAs might offer more flexibility and tax benefits in retirement.
Investment Options
Investing in a Roth IRA or Traditional IRA can be a powerful way to save for retirement. Both offer unique benefits and tax advantages. One key factor to consider is the range of investment options available. Understanding these options can help maximize your retirement savings.
Fund Choices
Both Roth IRA and Traditional IRA accounts offer a wide range of investment choices. These include mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and ETFs. Each option has its own benefits and risks.
With a Roth IRA, your contributions are made with after-tax dollars. This means withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. A Traditional IRA, on the other hand, uses pre-tax dollars. This allows for tax-deductible contributions but taxes withdrawals in retirement.
Below is a table comparing the fund choices available for Roth IRA and Traditional IRA:
| Investment Type | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Mutual Funds | Available | Available |
| Stocks | Available | Available |
| Bonds | Available | Available |
| ETFs | Available | Available |
Choose funds based on your risk tolerance and retirement timeline. For instance, younger investors might prefer stocks for growth potential. Older investors might choose bonds for stability.
Diversification
Diversification is crucial in any investment strategy. It helps spread risk across different asset classes. Both Roth IRA and Traditional IRA accounts allow for a diversified portfolio.
Here are some ways to diversify your IRA investments:
- Invest in a mix of asset classes: Include stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
- Choose different sectors: Invest in technology, healthcare, and consumer goods.
- Include international investments: Consider global funds to diversify geographically.
Diversification reduces the impact of poor performance in any single investment. A well-diversified Roth IRA or Traditional IRA can provide more stable returns over time.
Consider using target-date funds. These funds automatically adjust the investment mix as you approach retirement. This can make diversification easier, especially for those who prefer a hands-off approach.
Credit: www.voya.com
Tax Benefits
Roth IRA and Traditional IRA offer great tax benefits. These benefits help you save for retirement in a smart way. Both types of IRAs have unique advantages. Understanding these benefits helps you choose the right IRA for your needs.
Immediate Deductions
One of the main tax benefits of a Traditional IRA is immediate deductions. Contributions to a Traditional IRA can be tax-deductible. This means you lower your taxable income for the year.
For example:
- If you contribute $6,000 to your Traditional IRA, your taxable income reduces by $6,000.
- This helps you pay less in taxes that year.
There are some rules to keep in mind:
- Your deduction amount may depend on your income and whether you have a retirement plan at work.
- If you or your spouse have a work plan, income limits may reduce your deduction.
Here’s a quick comparison table to make it clearer:
| Factor | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|
| Deduction | May be fully or partially deductible |
| Income Limits | Applies if you have a retirement plan at work |
| Immediate Tax Benefit | Yes |
Tax-free Growth
The tax-free growth feature is a major benefit of Roth IRAs. In a Roth IRA, your contributions are made with after-tax dollars. This means you do not get an immediate tax deduction.
But, the real benefit comes later. Your investments grow tax-free. This means:
- You do not pay taxes on investment gains.
- Withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Contribute after-tax dollars to your Roth IRA.
- Your investments grow without any tax on the earnings.
- Withdraw funds tax-free in retirement.
Imagine your Roth IRA grows from $6,000 to $10,000. You do not owe taxes on the $4,000 gain. This tax-free growth can be a huge advantage, especially if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
Here’s a comparison table for clarity:
| Factor | Roth IRA |
|---|---|
| Immediate Deduction | No |
| Tax on Growth | No |
| Tax on Withdrawals | No (if conditions are met) |
Estate Planning
Choosing between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA is crucial for effective estate planning. Each option has unique benefits and drawbacks that can significantly impact your legacy. Understanding the differences in beneficiary designation and tax implications can help you make an informed decision.
Beneficiary Designation
When designating beneficiaries for your Roth IRA or Traditional IRA, there are a few key differences to keep in mind. Roth IRAs offer more flexibility for your heirs. Beneficiaries can receive tax-free distributions, provided the account has been open for at least five years. This can be a significant benefit for your loved ones.
With a Traditional IRA, beneficiaries will still have to pay taxes on the distributions they receive. This could potentially reduce the amount of inheritance they receive. It’s important to choose your beneficiaries carefully to ensure that your assets are distributed according to your wishes.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Roth IRA: Tax-free distributions for beneficiaries.
- Traditional IRA: Beneficiaries pay taxes on distributions.
- Flexibility: Roth IRAs offer more flexibility in terms of tax-free benefits.
Below is a table summarizing the differences:
| IRA Type | Beneficiary Tax Implications | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Roth IRA | Tax-Free Distributions | High |
| Traditional IRA | Taxable Distributions | Low |
Tax Implications
Understanding the tax implications of Roth IRA and Traditional IRA is essential for estate planning. Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars. This means that your contributions are taxed before they go into the account. The benefit is that your beneficiaries can withdraw the funds tax-free.
Traditional IRAs, on the other hand, are funded with pre-tax dollars. This means you get a tax deduction on your contributions now, but your beneficiaries will pay taxes on the distributions later. This could potentially reduce the amount they receive from your estate.
Here are some key tax points to consider:
- Roth IRA: Funded with after-tax dollars; tax-free withdrawals for beneficiaries.
- Traditional IRA: Funded with pre-tax dollars; taxable distributions for beneficiaries.
- Tax Deductions: Immediate tax benefits for Traditional IRAs.
Below is a table summarizing the tax implications:
| IRA Type | Tax Treatment | Beneficiary Tax Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Roth IRA | After-Tax Contributions | Tax-Free Withdrawals |
| Traditional IRA | Pre-Tax Contributions | Taxable Withdrawals |
By understanding these differences, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your estate planning goals.

Credit: meldfinancial.com
Choosing The Right Option
Choosing between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA can significantly impact your retirement savings. Each option offers distinct benefits and has unique implications for your financial future. Understanding your circumstances and long-term goals can help you make an informed decision.
Individual Circumstances
Your individual circumstances play a crucial role in deciding between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Current Income: If you’re in a lower tax bracket today, a Roth IRA might be beneficial since you pay taxes now and enjoy tax-free withdrawals later.
- Future Tax Bracket: Expecting a higher tax bracket at retirement? A Roth IRA could be advantageous.
- Age: Younger individuals may benefit more from a Roth IRA due to the longer time horizon for tax-free growth.
- Income Limits: Roth IRAs have income limits for contributions. Check if your income qualifies.
- Immediate Tax Deduction: If you need a tax break now, a Traditional IRA can reduce your taxable income for the current year.
Here’s a quick comparison table:
| Factor | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Treatment | Contributions taxed, withdrawals tax-free | Contributions tax-deductible, withdrawals taxed |
| Income Limits | Yes | No |
| Age Limit for Contributions | No | Yes (70½) |
Long-term Goals
Considering your long-term goals is essential in the Roth IRA vs. Traditional IRA decision. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Retirement Age: Planning to retire early? A Roth IRA allows for penalty-free withdrawals of contributions anytime.
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Traditional IRAs require RMDs starting at age 72. Roth IRAs do not have RMDs during the account holder’s lifetime.
- Estate Planning: Roth IRAs can be advantageous for passing on wealth, as beneficiaries can receive tax-free distributions.
- Expected Expenses: If you anticipate high expenses in retirement, a Roth IRA provides tax-free income, which can be beneficial.
- Investment Growth: If you expect significant growth in your investments, a Roth IRA allows you to reap the benefits tax-free.
These considerations can help you align your IRA choice with your long-term financial goals. Understanding how each type of IRA aligns with your future plans ensures you maximize your retirement savings strategy.
Credit: alliancewealthadvisors.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is It Better To Do A Traditional Or Roth Ira?
Choosing between a Traditional and Roth IRA depends on your current and future tax situation. Traditional IRAs offer tax-deferred growth, while Roth IRAs provide tax-free withdrawals. Evaluate your income level and expected retirement tax bracket to decide which option benefits you more.
Consult a financial advisor for personalized advice.
Is A Roth Ira Better Than A Traditional Ira For 25 Year Old?
A Roth IRA often benefits a 25-year-old due to expected future tax savings. Contributions grow tax-free, and withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. It’s ideal for those in a lower tax bracket now.
Should I Be More Aggressive With Roth Or Traditional Ira?
Choose Roth IRA for tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Opt for traditional IRA for immediate tax deductions. Your choice depends on your current and future tax situations.
Is A 401k Or Ira Or Roth Ira Better?
The best choice depends on your financial goals. A 401(k) offers employer matches. IRAs provide flexible investment options. Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals.
Conclusion
Choosing between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA depends on your financial goals and tax preferences. Both offer unique benefits. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision. Evaluate your current and future tax situation to determine the best fit for your retirement planning.
Make the choice that aligns with your financial future.






Leave a Reply